Water Washed Kaolin VS Calcined Kaolin
Both washed kaolin and calcined kaolin belong to kaolin minerals. Water washed kaolin is obtained through washing and grading, and can be divided into low iron type, high iron type, and waste soil type. Calcined kaolin is a product obtained by high-temperature calcination of natural kaolin ore.

There are significant differences between calcined kaolin and washed kaolin in multiple aspects:
1. Processing Process
- Water Washed Kaolin: Add kaolin to water, stir, precipitate, and separate to remove impurities and useless substances, and obtain pure kaolin powder.
- Calcined Kaolin: Kaolin is roasted at high temperatures to undergo chemical reactions to improve its physical and chemical properties. This process will cause the kaolin to lose its crystalline water and form a fluffy porous sheet-like structure.
2. Chemical Composition
- Water Washed Kaolin: The main components of water washed kaolin are Al2O3 and silicates, with low iron content and stable chemical composition, which basically does not change.
- Calcined Kaolin: Calcined kaolin is rich in Al2O3, as well as varying degrees of iron oxide and sodium oxide. After calcination, the crystal structure and chemical composition of kaolin will change.
3. Physical Properties
- Water Washed Kaolin: Water washed kaolin has the characteristics of strong adsorption capacity, good fluidity, fine particle density, large specific surface area, and good air permeability.
- Calcined Kaolin: It has high thermal stability and compressive performance, with a larger particle size and smaller specific surface area.
4. Glossiness and Whiteness
- Water Washed Kaolin: The glossiness and whiteness usually do not increase significantly.
- Calcined Kaolin: The glossiness will increase, and the whiteness will also increase. The whiteness after calcination is more important, and the higher the whiteness, the better the quality.
Read Also: Analysis of 8 Whitening Methods for Kaolin
5. Adhesive Properties
- Water Washed Kaolin: It is only a physical treatment and will not change the characteristics of the original soil. The original soil has adhesive strength and can be directly used as a binder for refractory insulation materials or as a filler in the papermaking industry.
- Calcined Kaolin: After calcination, the crystal structure and original soil properties have changed. The original soil has no cohesive force and cannot be directly used as a raw material for the papermaking industry or refractory insulation materials.
6. Main Applications
- Water Washed Kaolin: suitable for manufacturing industries such as ceramics, rubber, coatings, and papermaking. The residual moisture content in washed kaolin is relatively high, making it unsuitable as an adsorbent material and filler.
- Calcined Kaolin: Due to its unique advantages of high activity, high whiteness, high dispersion, and high coverage, calcined kaolin is suitable as a catalyst and filler material. The four major fields of application of calcined kaolin are papermaking, paint coatings, rubber, and plastics.

7. Cost
- Water Washed Kaolin: The production of washed kaolin is relatively simple, requiring the crushing of raw materials first, followed by mixing, desliming, filtering, and drying with water, which can obtain relatively pure kaolin products in a short period of time. The cost is relatively low.
- Calcined Kaolin: To calcine kaolin, the raw materials need to be crushed first, and then preheated, high-temperature calcined, and cooled. The high-temperature calcination temperature is usually between 1200 ℃ and 1300 ℃. This production process requires a large amount of thermal energy and reaction time, and the production cost is relatively high.
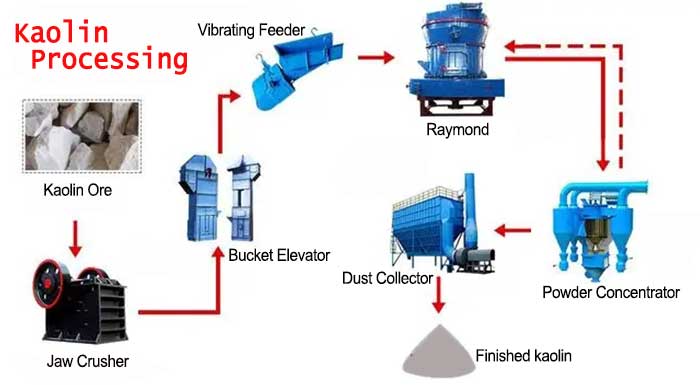 Kaolin Processing Plant | Water Washed Kaolin Process
Kaolin Processing Plant | Water Washed Kaolin Process Analysis of 8 Whitening Methods for Kaolin
Analysis of 8 Whitening Methods for Kaolin

