Analysis of 8 Whitening Methods for Kaolin
Kaolin, as a natural mineral widely used in ceramics, coatings, papermaking and other fields, its whiteness is an important indicator for measuring its quality. The whiteness not only determines the market price of kaolin, but also determines its wide and deep application. Therefore, improving the whiteness of kaolin and reducing the content of impurities such as iron and titanium has become a crucial step in the kaolin processing.

The following is the analysis of the whitening method for kaolin:
1. Water Washing for Whitening
This is a simple and direct physical whitening method. By washing kaolin with water to remove impurities and colored substances attached to the surface, the whiteness of kaolin is improved. During the washing process, dispersants such as sodium polyphosphate can be added to separate the particles in the flocs, further improving the washing effect.
Water washing whitening is suitable for kaolin with high surface impurities. Simple and direct, with lower cost.
2. Magnetic Separation Whitening
Magnetic separation whitening mainly utilizes the magnetic differences of impurity minerals in kaolin for separation. By using strong magnetic separators or superconducting magnetic separators, weak magnetic minerals such as iron oxides and ilmenite can be effectively removed from kaolin.

The magnetic separation process has the advantages of simple operation and low cost, and is particularly suitable for processing low-quality kaolin with high impurities.
3. Flotation Whitening
Flotation whitening utilizes the physical property differences between kaolin particles and gangue minerals for separation. The reverse flotation method adjusts the type and dosage of flotation reagents to cause kaolin particles to sink and gangue minerals to float, thereby achieving effective removal of impurities.
The flotation whitening technology is suitable for processing kaolin raw materials with high impurities and low whiteness, and can significantly improve the whiteness and purity of kaolin.
4. Coloring Bleaching
Color bleaching is the process of adding a white agent to kaolin to cover its surface, thereby increasing its whiteness. The chemicals used for coloring and bleaching include TiO2, CaSO4 · 2H2O, CaCO3, CaSiO3 · H2O, etc.
The advantages of this method are simple operation and low cost, but the bleaching effect is affected by factors such as the fineness of the agent and stirring speed. Therefore, in practical applications, it is necessary to strictly control the operating conditions to ensure the stability and consistency of the bleaching effect.
5. Reduction Bleaching
Reduction bleaching is the process of reducing Fe3+in kaolin to soluble Fe2+using a reducing agent, and then removing it through washing to improve the whiteness of kaolin. This is a traditional iron removal method in the kaolin industry. Commonly used reducing bleaching agents include sodium hydrosulfite (Na2S2O4) and thiourea dioxide (HO2SC (NH) NH2).

This method is suitable for processing kaolin with high iron content, which can significantly reduce iron content and improve whiteness. However, it should be noted that the selection and dosage of reducing agents need to be adjusted according to the actual situation to avoid pollution to the environment.
6. Acid leaching Bleaching
Acid leaching bleaching is the process of using an acid solution to react with insoluble compounds in kaolin, transforming them into soluble compounds and separating them from kaolin. Common acid solutions include hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, oxalic acid, etc.
This method is suitable for processing kaolin with a variety of impurities and complex occurrence states. In practical applications, it is necessary to select appropriate acid solutions and reaction conditions based on the types and occurrence states of impurities in kaolin to achieve the best bleaching effect.
7. Ion Exchange
By exchanging anionic exchange agents with specific functions with kaolin, the surface properties are improved.
This method is suitable for application scenarios that require high performance of kaolin. It can improve the dispersibility, wettability, and whitening properties of kaolin. The disadvantage is high cost and complex operation.
8. Baking Whitening
Baking whitening is the process of decomposing or transforming organic impurities and certain metal oxides in kaolin through high-temperature treatment, thereby improving the whiteness of kaolin. During the roasting process, different additives such as chlorinating agents and oxidants can be added to enhance the removal effect.

The roasting whitening technology is suitable for treating kaolin with high impurities such as carbon and sulfur, and can significantly improve the whiteness and purity of kaolin.
When choosing a kaolin whitening method, it is necessary to comprehensively consider multiple factors such as the properties of kaolin, iron content, whiteness target, cost, environmental impact, and production process. Choose the most suitable kaolin whitening method for yourself.
 Water Washed Kaolin VS Calcined Kaolin
Water Washed Kaolin VS Calcined Kaolin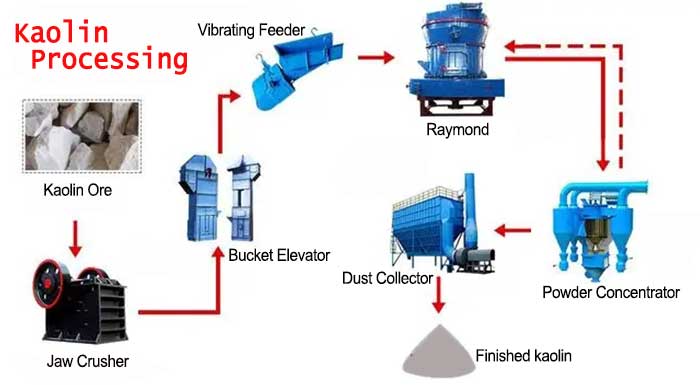 Kaolin Processing Plant | Water Washed Kaolin Process
Kaolin Processing Plant | Water Washed Kaolin Process 8 Methods for Removing Iron From Silica Sand
8 Methods for Removing Iron From Silica Sand Lithium Battery Recycling and Treatment Methods
Lithium Battery Recycling and Treatment Methods

