20 Common Types of Cement [Properties & Uses]
Cement is a powdery, hydraulic, inorganic cementitious material. After mixing with water, it forms a slurry that can harden in air or water, and can firmly bond materials such as sand and stone together. There are various types of cement on the market, and this article lists common types of cement and their uses.

Common Types and Properties of Cement (PDF DOWNLOAD)
(1) Silicate Cement
Hydraulic cementitious materials made of silicate cement clinker, 0%~5% limestone or granulated blast furnace slag and appropriate amount of gypsum grinding are called Portland cement, which is divided into P.I and P.II.
Use: Silicate cement is suitable for preparing high-strength grade concrete, pre tensioned prestressed products, roads, and construction projects at low temperatures. Not suitable for large volume concrete, projects subject to chemical and seawater erosion.
(2) Ordinary Portland Cement
Portland cement clinker, 6%~20% mixtures, and appropriate amount of gypsum grinding made of hydraulic cementitious materials, known as ordinary Portland cement (abbreviated as ordinary cement), code name: P.O.
Use: It has strong adaptability and can be used in projects without special requirements.
(3) Slag Cement
Hydraulic cementitious material made of Portland cement clinker, 20%~70% granulated blast furnace slag and appropriate amount of gypsum grinding is called Portland slag cement, code name: P.S.
Use: Suitable for various concrete projects on the ground and underground water, as well as high-temperature workshop buildings. Not suitable for projects that require early strength and freeze-thaw cycles or wet dry alternation.
(4) Pozzolanic Cement
Portland cement clinker, 20%~40% pozzolanic mixing and appropriate amount of gypsum grinding made of water-hard cementitious materials, known as volcanic ash Portland cement, code name: P.P.
Use: Suitable for underground and water engineering, large volume concrete engineering, general industrial and civil construction. Not suitable for projects that require early strength, freeze-thaw cycles, or wet dry alternation.

(5) Fly Ash Cement
Portland cement clinker, 20%~40% fly ash and appropriate amount of gypsum grinding made of water-hard cementitious materials, known as Portland-fly ash cement, code name: P.F.
Use: Suitable for large volume concrete engineering, underground engineering, general industrial and civil construction. Not applicable to the same scope as slag cement.
(6) Hydrophobic Cement
Hydrographic cement is made of the water repelling material that contain Ca, Al with the ordinary cement during the process of cement producing. Manily used for the structures: dams, water tanks, spillways etc.
Use: Hydrophobic cement is mainly used in construction projects that require waterproofing and moisture resistance.
(7) Composite Cement
Hydraulic cementitious materials made of Portland cement clinker, 20%~50% two or more specified mixtures and appropriate gypsum are called composite Portland cement (abbreviated as composite cement), code P.C.
Use: Suitable for general concrete engineering as well as industrial and civil construction engineering. Not suitable for corrosion-resistant engineering, use self compacting concrete with caution.
(8) Medium Heat Cement
Hydraulic cementitious material with moderate hydration heat is prepared by grinding Portland cement clinker with appropriate composition and adding appropriate amount of gypsum.
Use: Suitable for various road construction, such as highways, urban main roads, airport runways, etc. In addition, it is also suitable for underground tunnel construction and basement engineering. Its high strength and durability can effectively improve the service life of roads.
(9) Low Heat Cement
Hydraulic cementitious materials with low hydration heat are prepared by grinding Portland cement clinker with appropriate composition and adding appropriate amount of gypsum.
Use: Mainly used in dam concrete, with advantages in dry shrinkage, corrosion resistance, impact resistance, and wear resistance.
(10) Rapid Hardening Cement
Hydraulic cementitious materials with faster initial strength increase rate. The content of tricalcium silicate and tricalcium aluminate is higher than that of ordinary cement. It has large specific surface area, fast hardening and high initial strength. Mainly used in emergency repair engineering.
Use: Rapid hardening cement suitable for ground repair, surface and structural repair of bridges, dams, and channels. Construction of underground structures, such as concealed pipes, tunnels, and basements.

(11) Sulphates Resisting Cement
Cement with good sulphate corrosion resistance is made of Portland cement clinker, adding appropriate amount of gypsum. Mainly used to reduce the risk of sulphate attack on concrete.
Use: Sulfate resistant cement: mainly used in engineering projects such as seaports, water conservancy, underground, tunnels, culverts, roads, and bridge foundations that are subject to sulfate erosion.
(12) White Cement

White cement is white silicate cement. It is different from ordinary Portland cement in that it is made from limestone and clay, which contain less coloring impurities (such as iron oxide and manganese oxide), and is calcined with ash free raw materials (such as heavy oil, gas, natural gas), and impurities should be avoided during the manufacturing process.
Due to the high cost and lack of additives to improve the initial and final setting time, the use in engineering is greatly restricted, so it is generally only used for decoration and not in engineering. Mixing alkaline resistant inorganic pigments into white cement can yield colored cement, which is also used as a decorative material.
Use: White cement mainly used for putty powder, coatings, joint fillers, binders, waterproof coatings, terrazzo, artificial stones, floor tiles, permeable bricks, washed stones, sculptures, wear-resistant floors, and colored cement.
(13) Road Cement
Which is made by grinding of Portland cement clinker, 0%~10% active mixture material and appropriate gypsum, is called Portland Road cement (referred to as road cement).
Use: Road cement widely used in road construction, mainly for making cement pavement, cement base layer, cement ground, and cement channels.
(14) Masonry Cement
The low-grade cement mainly used for masonry mortar is made from active mixtures, Portland cement clinker and gypsum.
Use: Masonry cement mainly used for masonry and plastering mortar, cushion concrete, etc. in industrial and civil buildings, and cannot be used for reinforced concrete or structural concrete.
(15) Oil Well Cement
Portland cement clinker, gypsum and mixtures made of suitable minerals are suitable for cementing oil and gas wells at a certain well temperature.
Use: Oil well cement mainly used for sealing and cementing engineering of oil and natural gas wells.
(16) Gypsum Slag Cement
The granulated blast furnace slag is used as the main component material, and the cement is made by adding appropriate amount of gypsum, Portland cement clinker or lime.
Use: Gypsum slag cement with good corrosion resistance and durability, it is mainly used for plastering mortar and cementitious materials in industrial buildings.
(17) Expansive Cement
This type cement will not shrink during and after hardening. Just expands slightly with time. Expansion cement is mainly used to produce waterproof mortar and waterproof concrete. It is suitable for reinforcing structure, pouring machine base or consolidating foot bolts.
Use: Expansive cement mainly used for concrete structures that require compensation for shrinkage, such as large volume concrete, large-area concrete, etc.

(18) High Alumina Cement
High alumina cement is a kind of cementitious material with rapid hardening, high strength, heat resistance and corrosion resistance. High alumina cement is mainly used in urgent projects, such as road and special emergency repairs, etc. It can also be used in winter construction projects.
Use: High alumina cement mainly used in high-temperature industrial fields such as refractory materials and castables, with high strength and good high-temperature resistance.
(19) Colored cement
Colored cement is a special type of cement, also known as colored Portland cement. It is made on the basis of ordinary Portland cement, with the addition of pigments and other auxiliary materials.
Use: Colored cement is mainly used in building decoration engineering and is commonly used to prepare various decorative concrete and mortar, such as terrazzo, terrazzo, artificial marble, etc. Compared with ordinary Portland cement, colored cement is more diverse in color and can add aesthetics and artistic sense to buildings.
(20) Aerated cement
Air entrained cement improves the performance of concrete by introducing a large number of tiny bubbles. These bubbles are generated by adding air entraining agents to cement or through certain process conditions.
Use: Air entrained cement is mainly used to solve the durability problems of concrete, such as frost resistance, impermeability, and corrosion resistance. In addition, air entrained cement can also improve the frost resistance of concrete, which is particularly important for applications in cold regions.
 How To Classify Cement ?
How To Classify Cement ? How To Classify Concrete [Classification, Manufacturing & Properties]
How To Classify Concrete [Classification, Manufacturing & Properties] Cement VS Concrete [8 Difference Between Cement and Concrete]
Cement VS Concrete [8 Difference Between Cement and Concrete]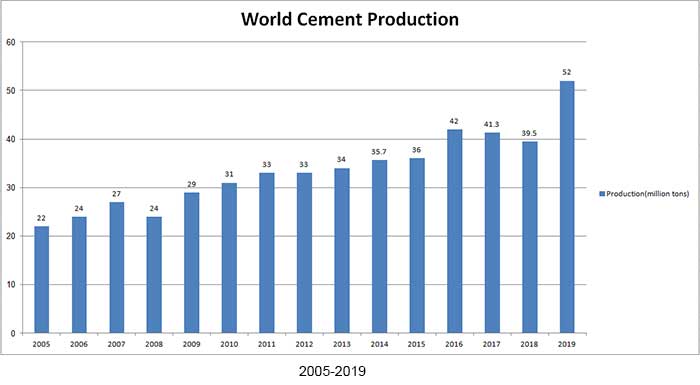 The Development of Cement History (1756 – 2019)
The Development of Cement History (1756 – 2019)

